That is at time the saying, it isn’t always ‘meant’ in a positive sight and it is for you to decide what it is now. The Deutsche Welle gave me yesterday an article that made me pause. It was in part what I have been saying all along. This doesn’t mean it is therefor true, but I feel that the tone of the article matches my settings. The article (at https://www.dw.com/en/german-police-expands-use-of-palantir-surveillance-software/a-73497117) giving us ‘German police expands use of Palantir surveillance software’ doesn’t seem too interesting for anyone but the local population in Germany. But that would be erroneous. You see, if this works in Germany other nations will be eager to step in. I reckon that The Dutch police might be hopping to get involved from the earliest notion. The British and a few others will see the benefit. Yet, what am I referring to?
It sounds that there is more and there is. The article’s byline gives us the goods. The quote is “Police and spy agencies are keen to combat criminality and terrorism with artificial intelligence. But critics say the CIA-funded Palantir surveillance software enables “predictive policing.”” It is the second part that gives the goods. “predictive policing” is the term used here and it supports my thoughts from the very beginning (at least 2 years ago). You see, AI doesn’t exist. What there is (DML and LLM) are tools, really good tools, but it isn’t AI. And it is the setting of ‘predictive’ that takes the cake. You see, at present AI cannot make real jumps, cannot think things through. It is ‘hindered’ by the data it has and that is why at present its track record is not that great. And there are elements all out there, there is the famous Australian case where “Australian lawyer caught using ChatGPT filed court documents referencing ‘non-existent’ cases” there is the simple setting where an actor was claimed to have been in a movie before he was born and the lists goes on. You see, AI is novel, new and players can use AI towards the blame game. With DML the blame goes to the programmer. And as I personally see “predictive policing” is the simple setting that any reference is made when it has already happened. In layman’s terms. Get a bank robber trained in grand theft auto, the AI will not see him as he has never done this. The AI goes looking in the wrong corner of the database and it will not find anything. It is likely he can only get away with this once and the AI in the meantime will accuse any GTA persona that fits the description.
So why this?
The simple truth is that the Palantir solution will safe resources and that is in play. Police forces all over Europe are stretched thin and they (almost desperately) need this solution. It comes with a hidden setting that all data requires verification. DW also gives us “The hacker association Chaos Computer Club supports the constitutional complaint against Bavaria. Its spokesperson, Constanze Kurz, spoke of a “Palantir dragnet investigation” in which police were linking separately stored data for very different purposes than those originally intended.” I cannot disagree (mainly because I don’t know enough) but it seems correct. This doesn’t mean that it is wrong, but there are issues with verification and with the stage of how the data was acquired. Acquired data doesn’t mean wrong data, but it does leave the user with optional wrong connections to what the data is seeing and what the sight is based on. This requires a little explanation.
Lets take two examples
In example one we have a peoples database and phone records. They can be matched so that we have links.
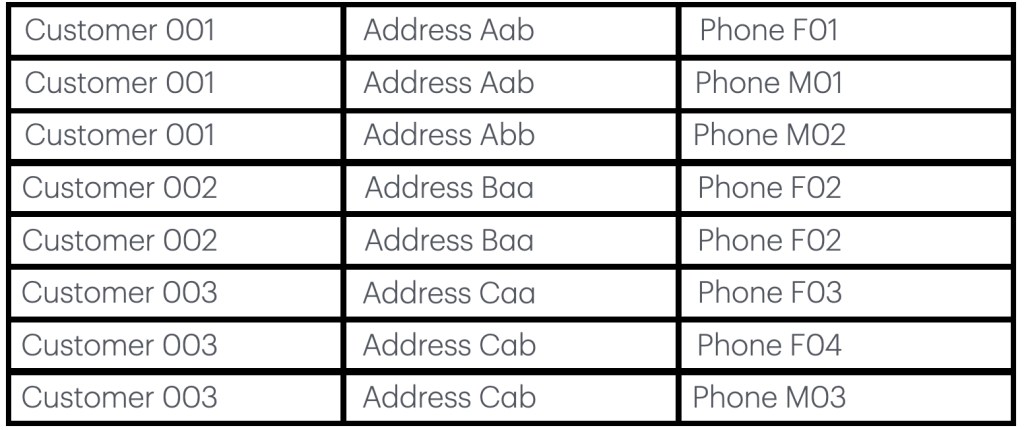
Here we have a customer database. It is a cumulative phonebook. All the numbers from when Herr Gothenburg got his fixed line connection with the first phone provider until today, as such we have multiple entries for every person, in addition to this is the second setting that their mobiles are also registered. As such the first person moved at some point and he either has two mobiles, or he changed mobile provider. The second person has two entries (seemingly all the same) and person moved to another address and as such he got a new fixed line and he has one mobile. It seems straight forward, but there is a snag (there always is). The snag is that entry errors are made and there is no real verification, this is implied with customer 2, the other option is that this was a woman and she got married, as such she had a name change and that is not shown here. The additional issue is that Müller (miller), is shared by around 700,000 people in Germany. So there is a likelihood that wrongly matched names are found in that database. The larger issue is that these lists are mainly ‘human’ checked and as such they will have errors. Something as simple as a phonebook will have its issues.
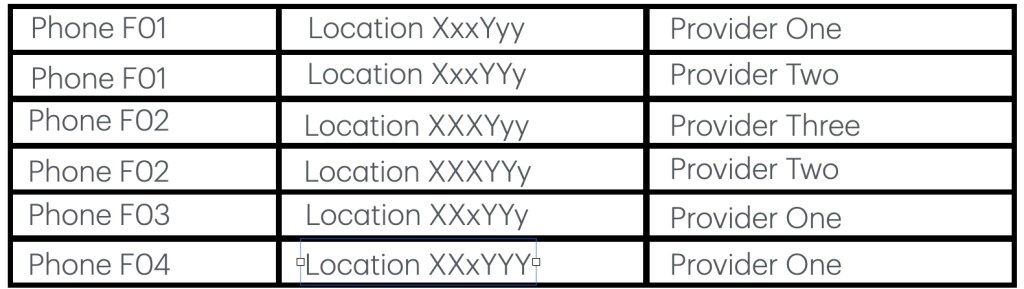
Then we get the second database which is a list of fixed line connections, the place where they are connected and which provider. So we get additional errors introduced for example, customer 2 is seemingly assumed to be a woman who got married and had her name changed. When was that, in addition there is a location change, something that the first database does not support as well as she changed her fixed line to another provider. So we have 5 issues in this small list and this is merely from 8 connected records. Now, DML can be programmed to see through most of this and that is fine. DML is awesome. But consider what some called AI and it is done on unverified (read: error prone) records. It becomes a mess really fast and it will lead to wrong connections and optionally innocent people will suddenly get a request to ‘correct’ what was never correctly interpreted.
As such we get a darker taint of “predictive policing” and the term that will come to all is “Guilty until proven innocent” a term we never accepted and one that comes with hidden flaws all over the field. Constanze Kurz makes a few additional setting, settings which I can understand, but also hindered with my lack of localised knowledge. In addition we are given “One of these was the attack on the Israeli consulate in Munich in September 2024. The deputy chairman of the Police Union, Alexander Poitz, explained that automated data analysis made it possible to identify certain perpetrators’ movements and provide officers with accurate conclusions about their planned actions.” It is possible and likely that this happens and there are intentional settings that will aide, optionally a lot quicker than not using Palantir. And Palantir can crunch data 24:7 that is the hidden gem in this. I personally fear that unless an accent to verification is made, the danger becomes that this solution becomes a lot less reliable. On the other hand data can be crushed whilst the police force is snoring the darkness away and they get a fresh start with results in their inbox. There is no doubt that this is the gain for the local police force and that is good (to some degree). As long as everyone accepts and realizes that “predictive policing” comes with soft spots and unverifiable problems and I merely am looking at the easiest setting. Add car rental data with errors from handwritings and you have a much larger problem. Add the risk of a stolen or forged drivers license and “predictive policing” becomes the achilles heel that the police wasn’t ready for and with that this solution will give the wrong connections, or worse not give any connection at all. Still, Palantir is likely to be a solution, if it is properly aligned with its strengths and weaknesses. As I personally see it, this is one setting where the SWOT solution applies. Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats are the settings any Palantir solution needs and as I personally see it, Weakness and Threats require its own scenario in assessing. Politicians are likely to focus on Strength and Opportunity and diminish the danger that these other two elements bring. Even as DW gives us “an appeal for politicians to stop the use of the software in Germany was signed by more than 264,000 people within a week, as of July 30.” Yet if 225,000 of these signatures are ‘career criminals’ Germany is nowhere at present.
Have a great day. People in Vancouver are starting their Tuesday breakfast and I am now a mere 25 minutes from Wednesday.






X to the power of sneaky
I was honestly a little surprised this morning when I saw the news pass by. The BBC (at https://www.bbc.co.uk/news/technology-67137773) gives us ‘Twitter glitch allows CIA informant channel to be hijacked’. To be honest, I have no idea why they would take this road, but part of me gets it. Perhaps in the stream of all those messages, a few messages might never be noticed. The best way to hide a needly is to drop it in a haystack. Yet the article gives us “But Kevin McSheehan was able to redirect potential CIA contacts to his own Telegram channel” giving us a very different setting to the next course of a meal they cannot afford. So when we are given “At some point after 27 September, the CIA had added to its X profile page a link – https://t.me/securelycontactingcia – to its Telegram channel containing information about contacting the organisation on the dark net and through other secretive means”, most of us will overlook the very setting that we see here and it took me hours to trip over myself and take a walk on the previous street to reconsider this. So when we are given “a flaw in how X displays some links meant the full web address had been truncated to https://t.me/securelycont – an unused Telegram username” the danger becomes a lot more visible. And my first thought was that a civilian named McSheehan saw this and the NSA did not? How come the NSA missed this? I think that checking its own intelligence systems is a number one is stopping foreign powers to succeed there and that was either not done, or the failing is a lot bigger then just Twitter. So even as the article ends with “The CIA did not reply to a BBC News request for comment – but within an hour of the request, the mistake had been corrected” we should see the beginning not the end of something. So, it was a set of bungles that starts with the CIA IT department, that goes straight into the NSA servers, Defence Cyber command and optionally the FBI cyber routines as well. You see, the origin I grasp at is “Installation of your defences against enemy retaliation” and it is not new, It goes back to Julius Caesar around 52BC (yes, more then two millennia ago). If I remember it correctly he wrote about it in Commentarii de Bello Gallico. Make sure your defences are secure before you lash out is a more up to date setting and here American intelligence seemingly failed.
Now, we get it mistakes will be made, that happens. But for the IT department of several intelligence departments to miss it and for a civilian in Maine to pick it up is a bit drastic an error and that needs to be said. This is not some Common Cyber Sense setting, this is a simple mistake, one that any joker could make, I get that. My issue is that the larger collection of intelligence departments missed it too and now we have a new clambake.
Yes, the CIA can spin this however they want, but the quote “within an hour of the request, the mistake had been corrected” implies that they had not seen this and optionally have made marked targets of whomever has linked their allegiance to the CIA. That is not a good thing and it is a setting where (according to Sun Tzu) dead spies are created. Yet they are now no longer in service of America, but they are optionally in service of the enemies of the USA and I cannot recall a setting where that ever was a good thing. You see, there was a stage that resembles this. In 942 the Germans instigated Englandspiel. A setting where “the Abwehr (German military intelligence) from 1942 to 1944 during World War II. German forces captured Allied resistance agents operating in the Netherlands and used the agents’ codes to dupe the United Kingdom’s clandestine organisation, the Special Operations Executive (SOE), into continuing to infiltrate agents, weapons, and supplies into the Netherlands. The Germans captured nearly all the agents and weapons sent by the United Kingdom” For two years the Germans had the upper hand, for two years the SOE got the short end of that stick and this might not be the same, but there is a setting where this could end up being the same and I cannot see that being a good thing for anyone (except the enemies of America). Now, I will not speculate on the possible damage and I cannot speculate on the danger optional new informants face or the value of their intelligence. Yet at this point I think that America needs to take a hard look at the setting that they played debutante too. I get it, it is not clear water, with any intelligence operation it never is. Yet having a long conversation with the other cyber units is not the worst idea to have. You see, there is a chance someone copied the CIA idea and did EXACTLY the same thing somewhere else. As such how much danger is the intelligence apparatus in? Come to think of it, if Palantir systems monitor certain server actions, how did they miss it too? This is not an accusation, it is not up to Palantir to patrol the CIA, but these systems are used to monitor social media and no one picked up on this?
Just a thought to have on the middle of this week.
Leave a comment
Filed under IT, Military
Tagged as Abwehr, BBC, CIA, Commentarii de Bello Gallico, Common Cyber Sense, DoD, Englandspiel, FBI, Julius Caesar, Kevin McSheehan, Maine, NSA, Palantir, SOE, Special Operations Executive, Sun Tzu, Twitter